Why is the GRE Exam Required?
Universities require it to assess a candidate’s readiness for advanced studies by evaluating:
Analytical Writing Skills – Ability to construct and analyse arguments.
Verbal Reasoning Skills – Vocabulary, reading comprehension, and critical thinking.
Quantitative Reasoning Skills – Basic math, data interpretation, and problem-solving.
Where is the GRE Exam Required?
The GRE is widely accepted in:
United States – Required for most Master’s & PhD programs (STEM, humanities, business, etc.).
Canada – Some universities require it for graduate programs.
United Kingdom – Some universities, like Oxford & Cambridge, accept GRE scores for specific programs.
Europe – Certain programs in Germany, France, and other EU countries accept GRE.
Australia & New Zealand – Some universities require GRE for master’s and PhD programs.
India – Some top MBA programs (like ISB, IIMs Executive MBA) accept GRE instead of GMAT.
Singapore & Hong Kong – Many top universities consider GRE scores for graduate programs.
Who Needs to Take the GRE?
📌 Master’s Applicants – Most MS programs in the USA and some other countries require GRE.
📌 PhD Applicants – Many doctoral programs use GRE scores for admission.
📌 MBA Applicants – Some business schools accept GRE instead of GMAT.
📌 Scholarship Seekers – High GRE scores can help secure scholarships & assistantships.
Note: To maintain students’ safety and confidentiality, student names and details have been blurred.
Note: To maintain students’ safety and confidentiality, student names and details have been blurred.
GRE Scorecards
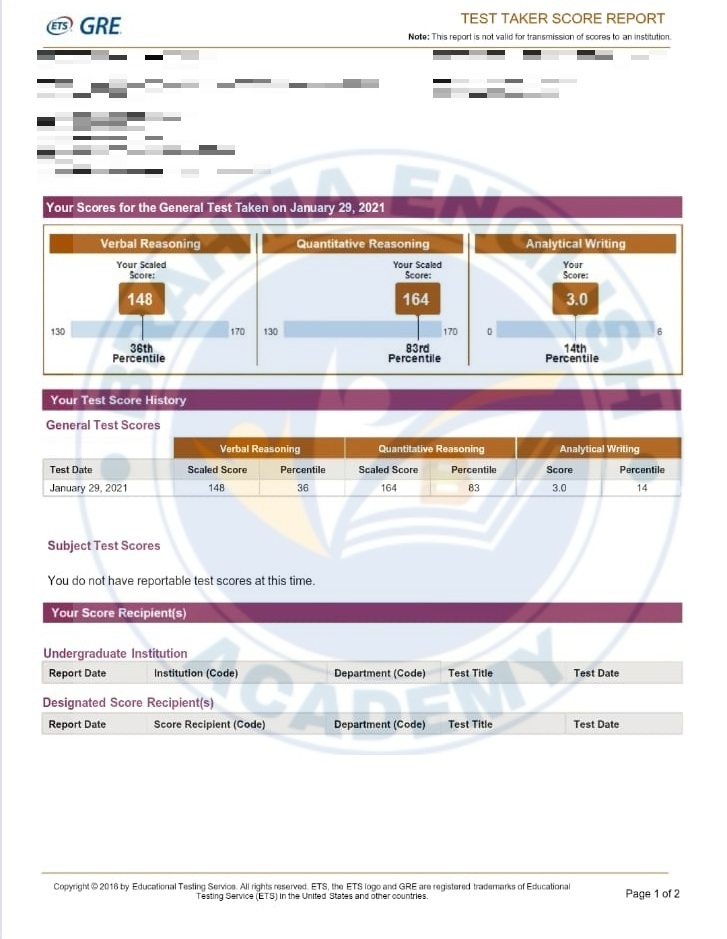
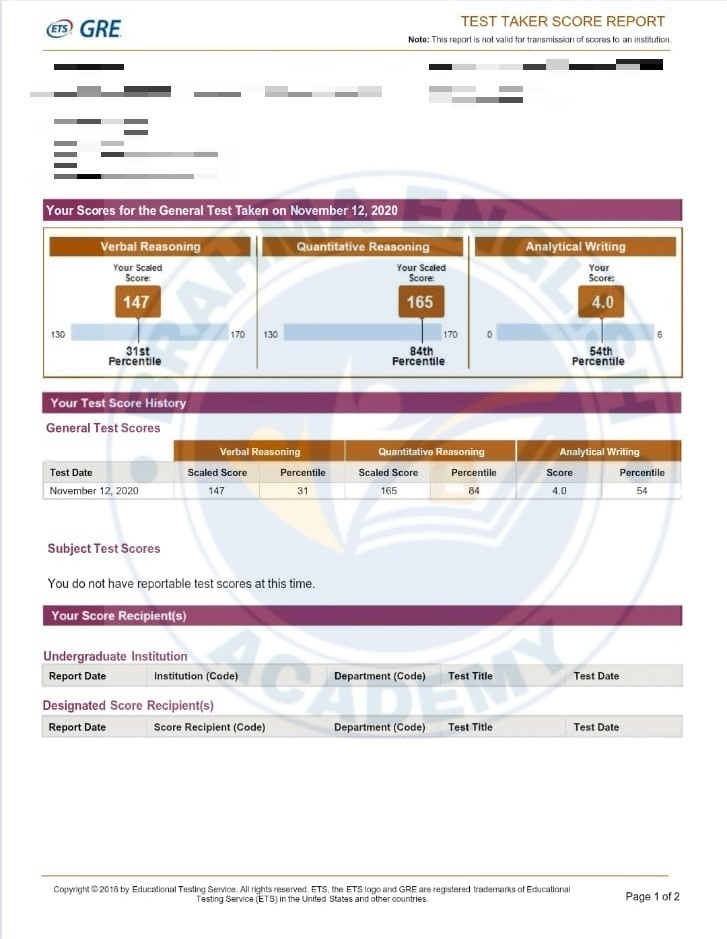
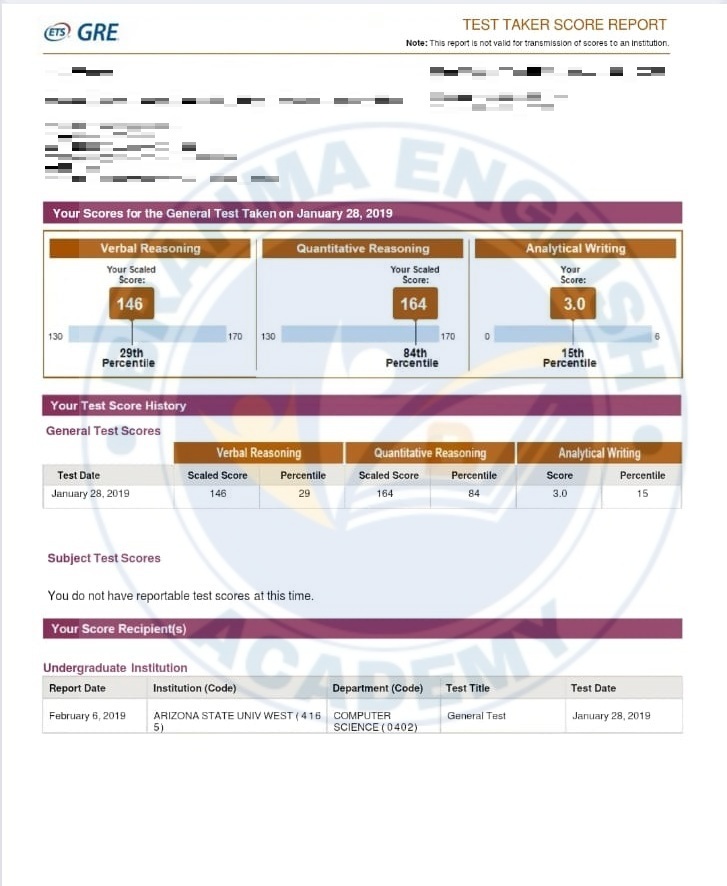
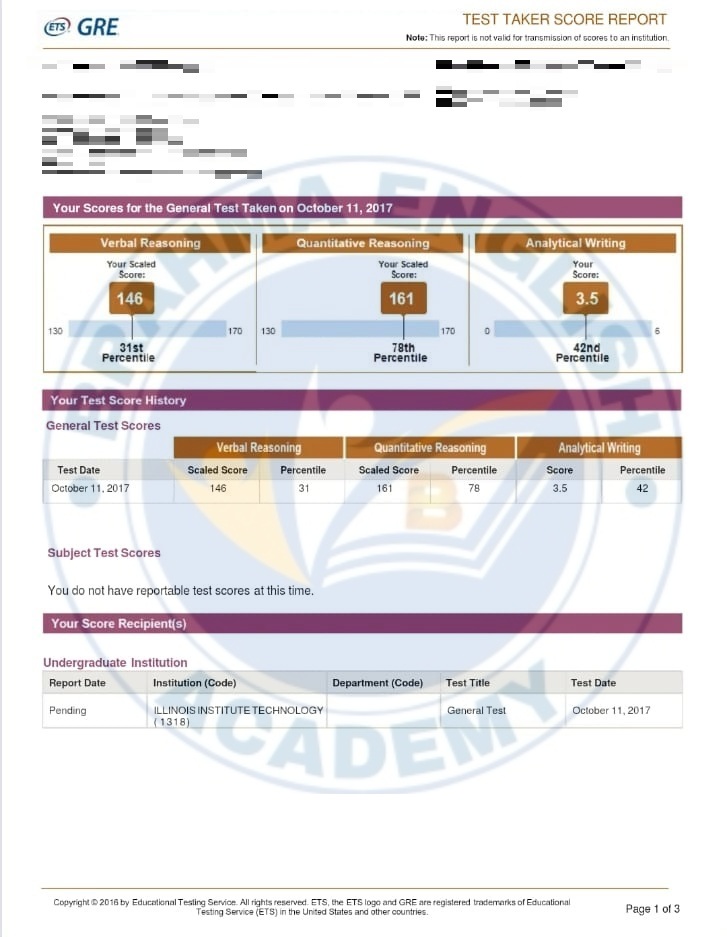
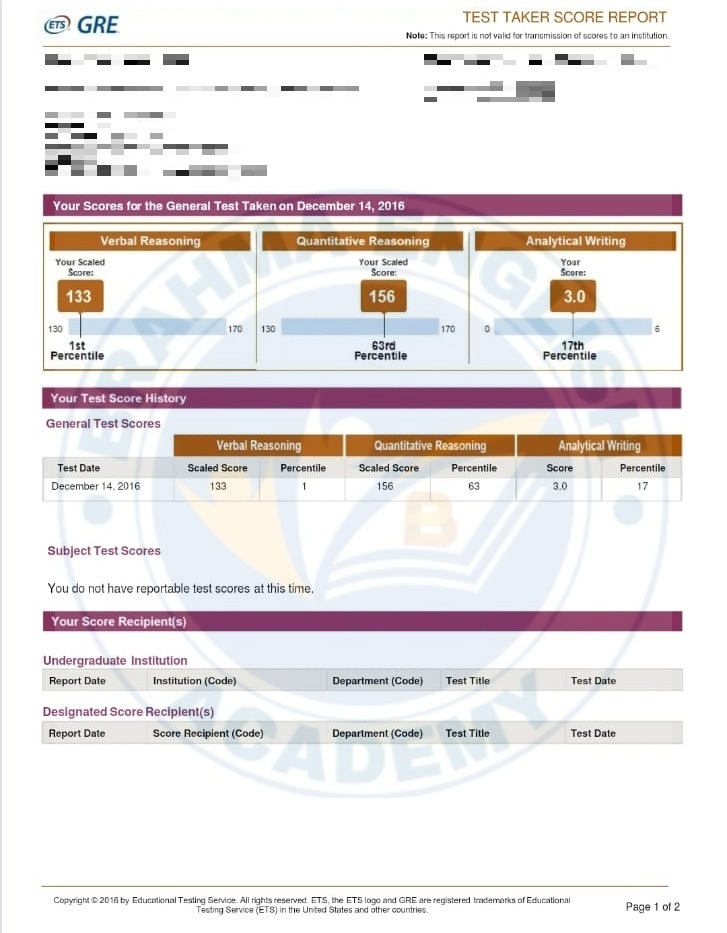

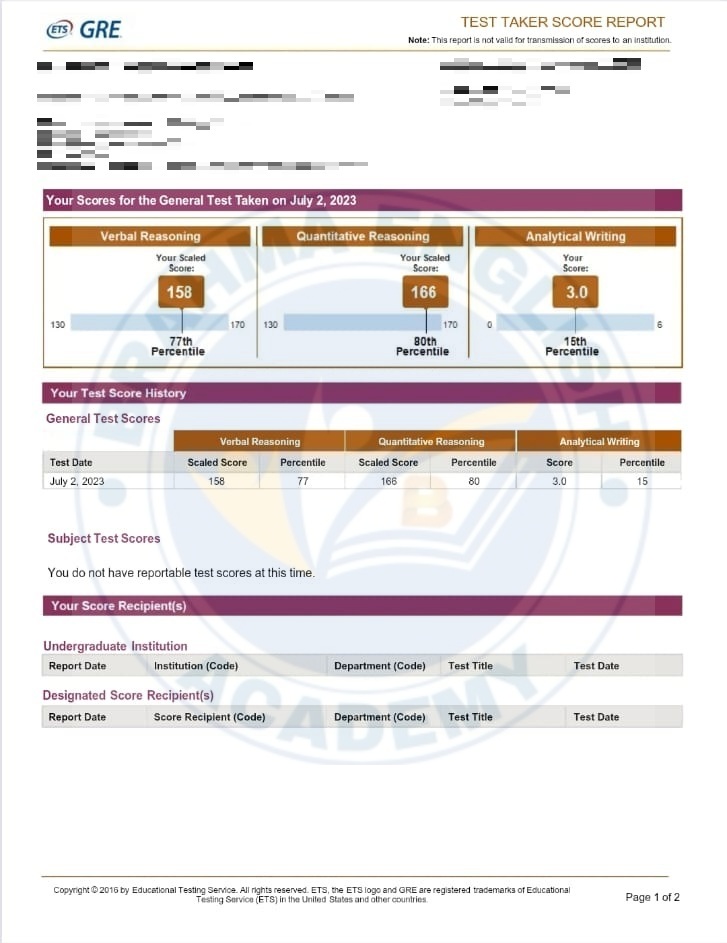
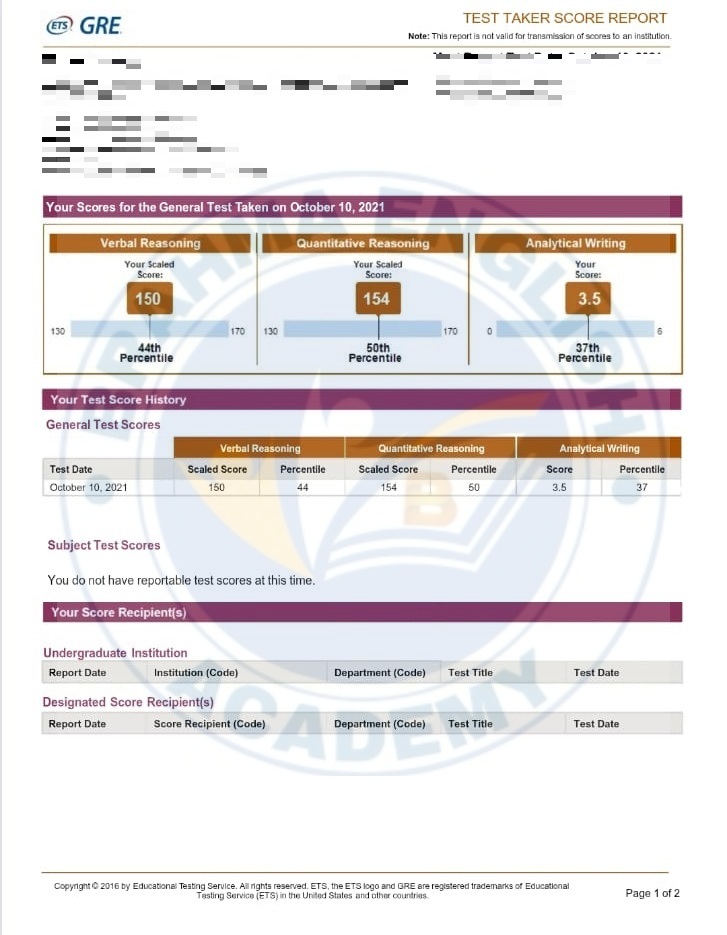
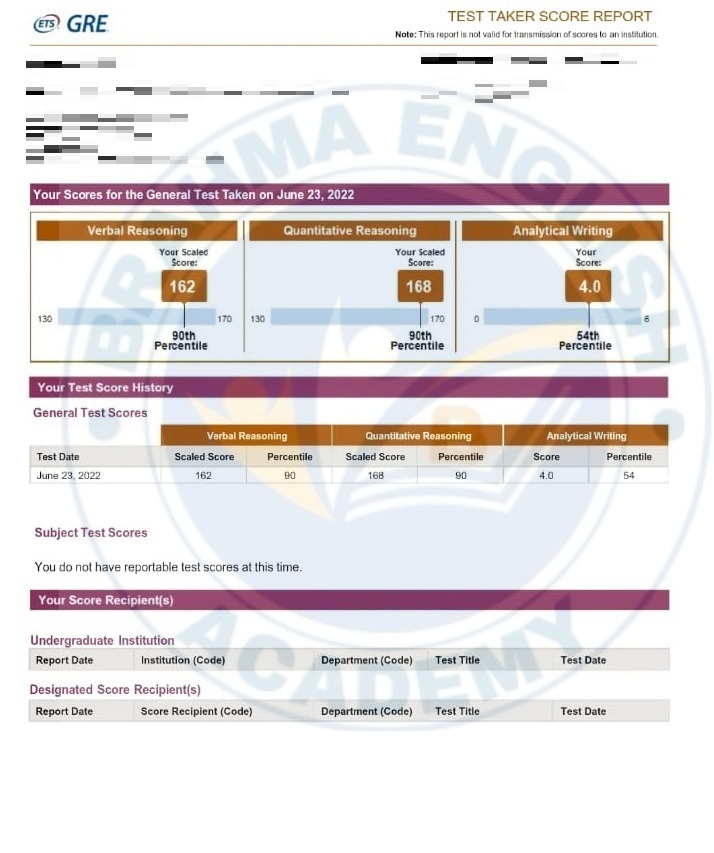
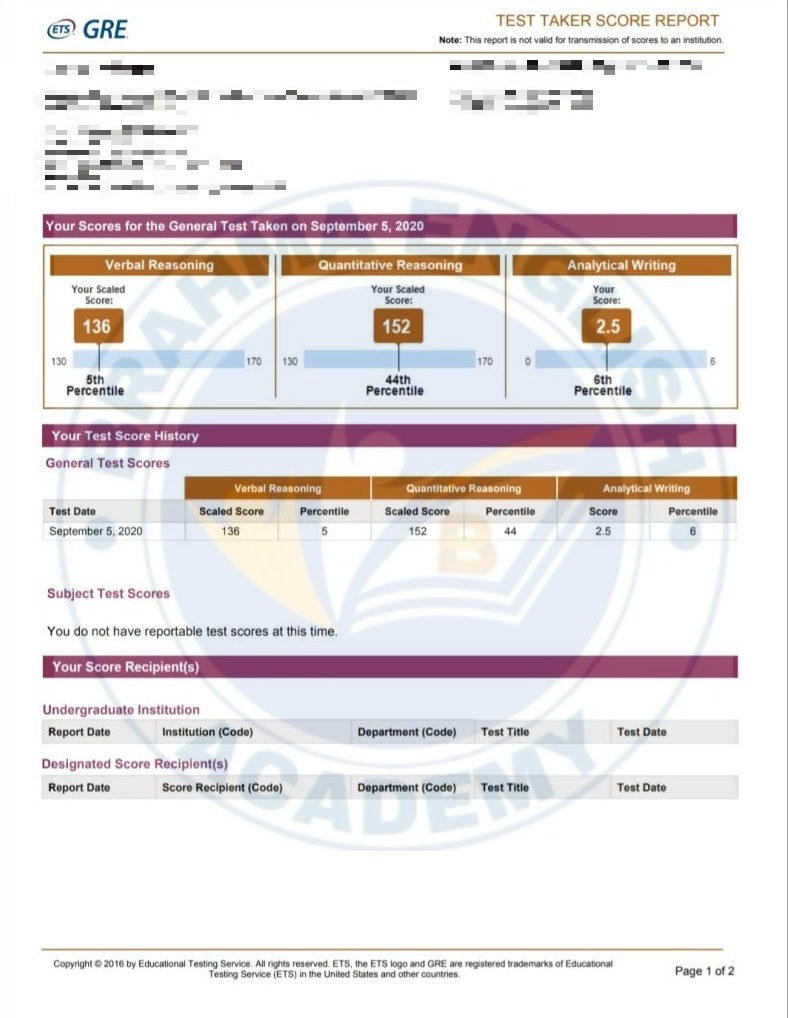
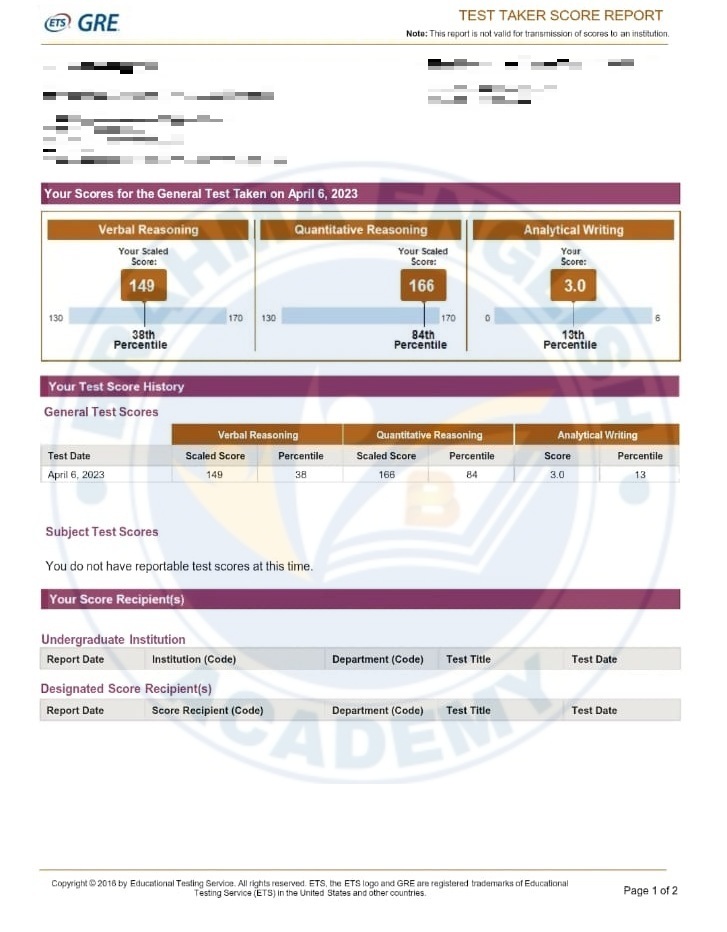
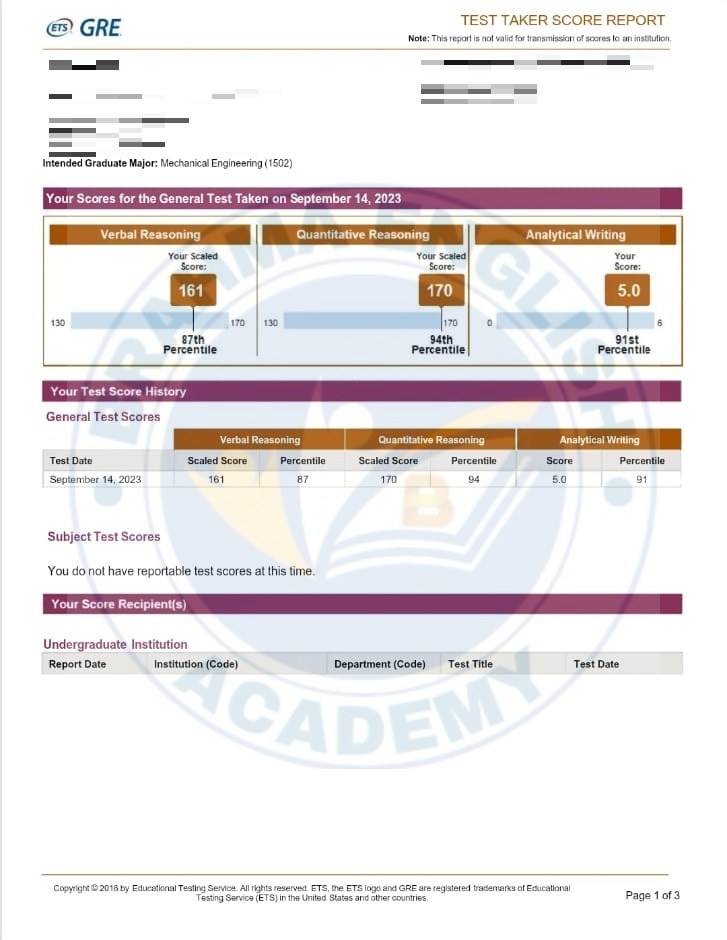
GRE Syllabus in Detail
The Graduate Record Examination (GRE) is a standardized test required for admission to many graduate programs worldwide. The exam is designed to assess verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, and analytical writing skills.
1.Verbal Reasoning (English Language Skills & Reading Comprehension)
Number of Questions: 40 (20 per section)
Time per Section: 30 minutes
Total Time: 60 minutes
A.Reading Comprehension (RC)
This section tests your ability to understand, analyze, and interpret written texts.
Question Types:
- Multiple-choice questions (single answer) – Select one correct answer.
- Multiple-choice questions (multiple answers) – Select all correct answers.
- Select-in-Passage – Choose a sentence that best answers a given question.
B.Text Completion (TC)
Tests your ability to infer meaning and select the most appropriate words to complete sentences.
Question Format:
- A short passage with one, two, or three blanks.
- Each blank has three to five answer choices.
You must select the correct word for each blank.
C.Sentence Equivalence (SE)
Tests your ability to identify synonyms that complete a sentence with the same meaning.
Question Format:
- One sentence with one blank.
- Six answer choices (you must select two correct words).
The two selected words should give the same meaning to the sentence.
2.Quantitative Reasoning (Mathematics & Problem-Solving Skills)
Number of Questions: 40 (20 per section)
Time per Section: 35 minutes
Total Time: 70 minutes
A. Arithmetic
Properties of integers (odd, even, prime numbers)
Fractions, decimals, percentages, and ratios
Powers and roots
Absolute value
B. Algebra
Linear equations and inequalities
Quadratic equations
Functions and graphs
Exponents and logarithms
C. Geometry
Properties of lines, angles, triangles, circles
Coordinate geometry
Perimeter, area, volume
D. Data Analysis
Mean, median, mode, and standard deviation
Probability and combinatorics
Interpreting charts, graphs, and tables
3.Analytical Writing (AWA - Essay Writing Skills)
Number of Essays: 2
Total Time: 60 minutes (30 minutes per task)
A. Analyze an Issue
You will be given a statement or a general issue.
You must take a position (agree/disagree) and present a well-reasoned argument.
Example Prompt:
📌 “Governments should focus more on environmental policies than economic growth.”
💡 You must present arguments for or against this statement with examples.
B. Analyze an Argument
You will be given a short argument (with flaws in reasoning).
You must analyze its logical soundness and point out weaknesses.
Example Prompt:
📌 “A recent study found that students who study late at night score higher. Therefore, schools should start classes later in the day.”
💡 You must evaluate whether this argument is logically strong or flawed.
GRE Marking System (Scoring Pattern Explained)
Overall GRE Score Calculation
Section | Score Range | Scoring Increment |
|---|---|---|
Verbal Reasoning | 130 – 170 | 1-point |
Quantitative Reasoning | 130 – 170 | 1-point |
Analytical Writing | 0 – 6 | 0.5-point |
4. Key Takeaways
325+ → Required for top-tier universities.
310-320 → Good for mid-tier universities.
300-310 → Accepted by some universities.
Below 300 → Limited admission options, except for certain less competitive programs.